🌍 Nilesat The Leading Satellite in the Arab World

Nilesat is one of the most important communication satellites in the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) region. Since its launch in 1998, it has become the backbone of satellite broadcasting in the region, offering a wide range of services including television, radio, and internet. Known for its extensive coverage and reliability, Nilesat plays a crucial role in connecting millions of viewers, businesses, and institutions across the Arab world.
🚀 On the subject of Nilesat
Nilesat, operated by the Egyptian company Nilesat Satellite Communications, provides satellite broadcasting services to a wide range of customers across the Middle East, North Africa, and parts of Europe. The satellite allows for the transmission of television and radio signals, as well as data and internet services.
Nilesat’s fleet of satellites serves multiple purposes:
-
Broadcasting TV channels: Free-to-air and subscription-based channels.
-
Radio broadcasting: National and regional radio stations.
-
Data services: Internet access and other telecommunication services.
-
Corporate communications: For businesses and institutions requiring dedicated communication lines.
With several satellites in orbit, including Nilesat 101, Nilesat 102, and the more recent Nilesat 201, the network continues to grow in capacity and service offerings.
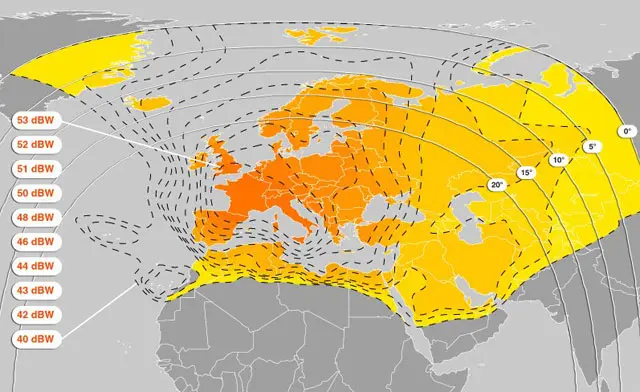
🌐 Nilesat’s Satellite Fleet
Nilesat operates a fleet of geostationary satellites positioned to serve the MENA region and beyond. These satellites are carefully positioned to provide the best possible signal coverage. Key satellites in the fleet include:
-
Nilesat 101
-
Nilesat 102
-
Nilesat 201
-
Nilesat 301 (upcoming)
These satellites are strategically placed to ensure seamless coverage for broadcasting TV channels, radio stations, and other telecommunication services.
🛰️ Frequencies and Services on Nilesat
Nilesat operates across various frequency bands, including the C-band and Ku-band. These frequencies are used for various services:
-
C-band: Primarily used for long-range communication and broadcasting, C-band offers a stable signal with less interference from weather conditions. It’s commonly used for television broadcasting.
-
Ku-band: This band is widely used for satellite TV broadcasting and internet services. The Ku-band offers higher capacity and smaller antennas, making it ideal for both residential and commercial use.
Nilesat also provides a variety of frequency ranges that enable users to access a broad array of channels and services. Users looking to set up satellite systems can find detailed guides to help them tune in to the correct frequencies.
📡 How to Receive Nilesat Signals
To access Nilesat’s satellite signals, users need a satellite dish and a receiver that supports the appropriate frequency bands (C-band or Ku-band).
The dish must be correctly aligned with the satellite’s orbital position for optimal signal reception. Once the dish is set up, users can enter the corresponding frequency in their receiver to access the desired channels.
Common Nilesat Frequencies:
-
Nilesat 101/102 Frequency:
-
Frequency: 11.977 GHz (Vertical)
-
Symbol Rate: 27500
-
FEC: 3/4
-
-
Nilesat 201 Frequency:
-
Frequency: 12.515 GHz (Horizontal)
-
Symbol Rate: 27500
-
FEC: 3/4
-
Users can access various TV channels, radio stations, and data services on these frequencies.
For easy access to these frequencies and satellite configurations, FreqSatellite is a reliable platform offering up-to-date information on Nilesat’s channels, frequencies, and settings.
Nilesat remains a vital asset for satellite communications and broadcasting in the Arab world.
With its broad coverage, extensive services, and reliable signal quality, it is a key player in delivering television, radio, and internet services to millions of people in the MENA region.
Whether you’re looking to set up a satellite system for personal or commercial use, Nilesat continues to provide top-notch services. For more information on frequencies and satellite settings, FreqSatellite offers the most comprehensive and current satellite guides.
Easy Channel Tuning Process
- Select the correct satellite before tuning.
- Ensure LNB settings match the satellite requirements.
- Insert frequency details exactly as listed.
- Scan and confirm the channel appears correctly.
Steps for Accurate Channel Installation
- Enter the installation menu on your receiver.
- Choose manual or advanced search mode.
- Input frequency, symbol rate, and polarization.
- Save the channel after confirming signal stability.
The Impact of Weather on Satellite TV Reception and How to Minimize It
Weather conditions can affect satellite TV reception, but proper measures can help maintain clear signals:
1. Rain and Snow
- Heavy rain or snow can weaken satellite signals, causing pixelation or temporary loss.
- Using a larger dish or a high-gain LNB can improve signal stability.
2. Strong Winds
- Wind may shift the dish, misaligning it from the satellite.
- Ensure the dish is firmly mounted with a secure bracket to prevent movement.
3. Sun Outages
- During certain times of the year, the sun can interfere with the satellite signal.
- Outages are temporary and typically last a few minutes per day over several days.
4. Preventive Measures
- Regularly check and tighten mounting brackets and cables.
- Keep the dish clear of debris, snow, or ice.
- Consider weather-resistant LNBs and dish covers for extreme conditions.
5. Signal Monitoring
- Use the receiver’s signal meter to monitor strength and make minor adjustments if needed.
65cm vs 90cm Satellite Dishes: Which One Is Right for You?
Choosing the right satellite dish size depends on your location, signal strength, and viewing needs:
65cm Dish
- Compact and easy to install, ideal for homes with limited space.
- Cost-effective and usually cheaper than larger dishes.
- Works well in areas with strong satellite signals.
- Less effective in weak signal areas or during adverse weather.
90cm Dish
- Larger surface captures more signal, providing better reception quality.
- Can receive distant satellites and low-power channels more effectively.
- More stable signal during rain, snow, or stormy weather.
- Requires more space and stronger mounting; generally more expensive.
The Future of Satellite Broadcasting: Trends in HD, 4K, and 8K TV
Satellite broadcasting continues to evolve, offering higher-quality content and innovative features for viewers worldwide:
1. HD and 4K Expansion
- High-definition (HD) and 4K channels are becoming standard, providing sharper images and enhanced sound.
- More broadcasters are adopting 4K to meet the growing demand for ultra-clear visuals.
2. Emerging 8K Broadcasting
- 8K TV offers ultra-high-resolution images with exceptional detail and realism.
- Satellite providers are exploring 8K broadcasts, though widespread adoption may take time due to bandwidth requirements.
3. Advanced Compression Technologies
- Efficient codecs like HEVC (H.265) allow high-resolution broadcasts with reduced bandwidth usage.
- Enables more HD, 4K, and future 8K channels to be transmitted via satellite efficiently.